The Value of Archive Satellite Imagery
In today’s data-driven world, the value of historical satellite imagery archives cannot be overstated. These archives hold a treasure trove of information spanning years, allowing businesses, researchers, and scientists to gain valuable insights, track changes, and make informed decisions. In this article, we’ll delve deeper into what it is, the significance of historical satellite imagery and the best practices for leveraging this invaluable resource.
What is Archive Satellite Imagery?
Before finding out the value of archive satellite imagery, you first have to understand what it is. Archive satellite imagery is a collection of historical satellite data that have already been captured. Many businesses, academics and even individuals use archive satellite imagery for a variety of purposes. For example, Digital Earth Australia, is a Government run program that uses satellite data to monitor Australia’s changing landscape through their Water Observations from Space service, which derive satellite images of Australia from 1987 to present day via Landsat 5, 7 and 8. This data aims to assist scientists to understand water trends and where it is usually present.
Types of Archive Satellite Imagery
In general satellite imagery comes in different resolutions which can cater to various project needs. These datasets can be categorised into four different resolutions;

- Low Resolution (>80m): These data sets can be used for a range of projects with Landsat providing free satellite imagery which cover a large landscape which you can access here.
- Medium Resolution (10 to 30): These datasets are typically utilised for regional or landscape analysis and visualisations. Landsat and Sentinel 2 are two examples of satellites which gather this imagery .
- High Spatial Resolution: These datasets are the most commonly used category of data.
By utilising platforms like Arlula, which enables you to catalog and access decades-long archives of high-quality satellite data, individuals and businesses can track environmental conditions, identify emerging trends, and further optimise their operations for maximum efficiency.
You can find more information on satellite imagery resolution and which one is right for your project needs here.
Archive Satellite Imagery Vs Satellite Tasking
The most significant difference between tasking and archive is the process. When tasking a satellite, the user must request and schedule a new image to be captured over a desired area of interest and time. Conversely, the archive is a passive collection of high-resolution satellite images, offering a wealth of previously captured data. You can read more here to find out which one is right for you.
The Significance of Satellite Data Archives
Satellite data archives provides a unique window into the past, enabling the analysis of environmental, social, and economic changes over time. By comparing past and present images, researchers can detect long-term trends, assess the impact of human activities, and monitor natural phenomena. This historical perspective is invaluable for understanding the dynamics of our planet and informing sustainable decision-making.
The Key Benefits of Archived Satellite Data
Satellite data archives are more than just a collection of old images. They serve as a powerful time machine, offering invaluable insights into changes and trends that have unfolded across the globe. Here’s how these archives unlock a wealth of benefits:


East England captured by Landsat 8 Thermal, 2023 and 2014.
Temporal Analysis
Unlike a single snapshot, archive imagery allows us to study environmental processes over extended periods. By analysing changes in vegetation cover, land use patterns, or glacial retreat, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of long-term environmental trends and predict future changes.
Here we’ve captured the thermal change of East England in 2023 and 2014 found on the Arlula Geostack Platform. This allows us to easily compare the heat change throughout the years and mitigate the risks of urban heat island effect.
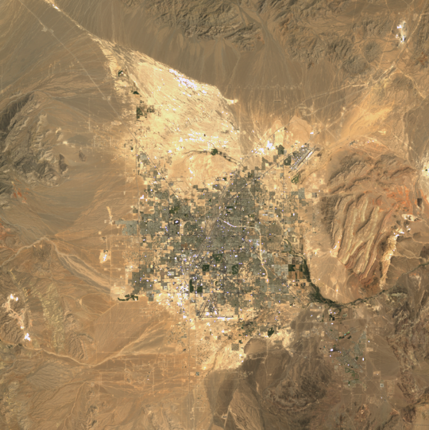

Arizona Sun City development captured by Landsat 4 in 1985 and Landsat 8 2024.
Infrastructure and Urban Development
Policymakers can use historical satellite imagery to evaluate the effectiveness of past policies related to land management, environmental protection, or urban development. By studying the consequences of past actions, policymakers can anticipate future challenges and develop evidence-based strategies for sustainable development that address the most pressing issues.
Through using archive imagery, we’re able to compare the vast development Arizona Sun City has had over the past few decades (1985 to 2024).
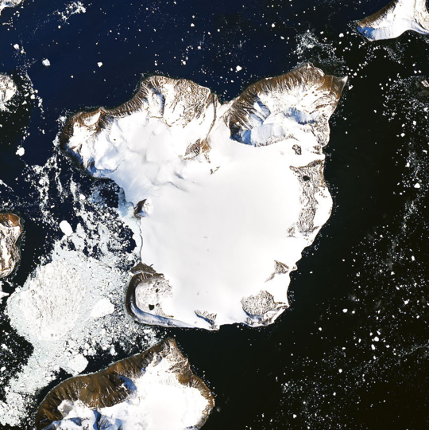
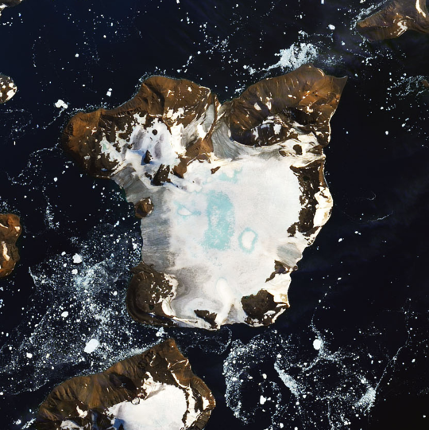


Ice Cap changes captured by Landsat 8, 2020
Climate change
Archive satellite data serves as a crucial tool for many within the environmental sector. By identifying changes in land use patterns or uncovering subtle features invisible to the naked eye, these experts can locate ancient sites and track cultural changes over time. This information is vital for preserving our collective heritage and safeguarding irreplaceable cultural artefacts.
One area where archive satellite imagery has assisted in environmental monitoring is within Antarctica. On February 6, 2020, Antarctica was recorded to have the hottest temperature on record. By using archive satellite imagery we can compare and monitor the extent of change, with the images above showcasing the melting on the ice cap of Eagle Island.
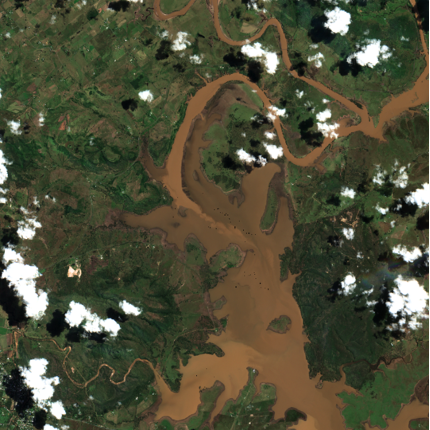
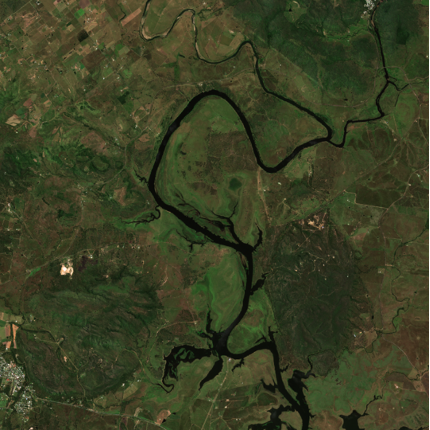

Flooding in Brisbane captured by Sentinel, 2022.
Disaster Preparedness
Historical satellite imagery plays a key role in disaster preparedness. It provides a valuable baseline for assessing the vulnerability of different regions to natural disasters. By analysing past events, emergency responders can identify areas at high risk of flooding, landslides, or earthquakes, enabling them to plan evacuation routes, prioritise mitigation efforts, and allocate resources effectively in the event of a disaster.
The above satellite images showcase the extent of flooding within Brisbane in 2022 which saw 177 suburbs impacted and 23,000 homes inundated.
Getting Started
Ultimately, archive satellite data serves as a bridge between the past, present, and future. It empowers us to learn from past environmental changes, make informed decisions in the present, and plan for a more sustainable future for our planet. Catalog and index petabytes of your organisations geospatial data with Arlula’s Geostack. This user-facing software makes your spatial data discoverable with simple search and index capabilities. Get started today to empower critical decisions with your satellite data.
Want to keep up-to-date?
Follow us on social media or sign up to our newsletter to keep up to date with new product releases and case studies.




