Finding Climate Solutions with Satellite Imagery
Our world experiences an ever changing climate. As the impacts of these changes have become more severe, tools to support our understanding and response are essential. Satellite imagery has emerged as a vital tool in monitoring and addressing land cover changes, human environmental impacts, future climate-related events and more. Here we will look at practical applications of satellite imagery data to the climate industry.
Monitor Land Cover Changes
Vegetation, particularly forests, play a critical role in climate regulation. Leverage available spectral bands to visualise features invisible to the human eye. High-resolution satellite imagery using derived bands such as NDVI and NDMI can provide insight into vegetation density in conservation habitats, water levels of a reservoir during drought, and fluctuations in ice cover in Arctic regions. Satellites enable coverage of large and hard to reach areas providing a complete picture of at-risk ecosystems and enhancing the ability to identify and monitor the impacts of climate change.
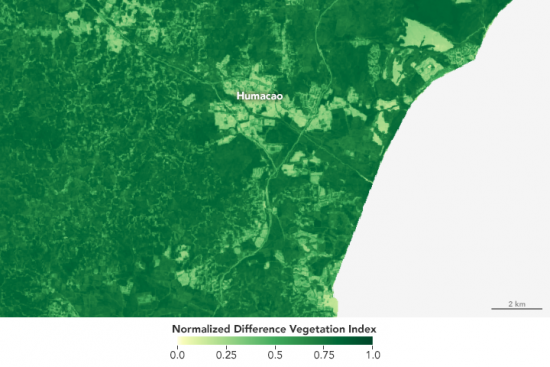
Captured by Landsat- 8 OLI December 2016.
Track Human Impacts


Development in Marsden Park, NSW from September 2017 (left) to December 2023 (right). Captured by Sentinel-2 l2A.
Efficiently track human activity in urban and rural areas by scheduling recurring image captures with tasking. Integrating satellite imagery with GIS software can help to identify and measure changes to features such as topography and vegetation volume as a result of deforestation, urbanisation, and resource extraction. Data collected can be used to monitor compliance, encourage climate action, and enhance decision making processes to maximise sustainability efforts. One problematic impact that humans have made is urban heat islands. Expanding urban networks, condensed city designs, decreased vegetation and the use of heat-absorbing materials in buildings and infrastructure contribute to the rising temperatures in urban areas. As global temperatures gradually increase, urban heat islands become more severe and the social and physical impact on communities within is greater. The use of thematic sensors to measure temperature, as well as other data such as SAR and optical imagery can provide tools to identify at-risk areas and develop solutions to create more liveable and sustainable cities.
Predict Future Changes
Utilise extensive Archive satellite imagery and new tasking imagery to assess weather and climate changes over decades. Track near-real time drought, flood, fire and weather conditions by scheduling recurring image captures with tasking. The data captured during these events can be used to predict and prepare for extreme climatic events in the future. Integrating new satellite imagery capture with existing sensors through Tip and Cue, provides an automated solution to identifying and monitoring changes. For example, bushfire detection. When smoke is detected by existing sensor systems, this triggers a “tip” action where a complementary sensor such as a satellite is “cued” to automatically task a higher resolution image of the area of interest. This ultimately improves the response time and decision making, minimising the risk to responders and impacts on civilians.
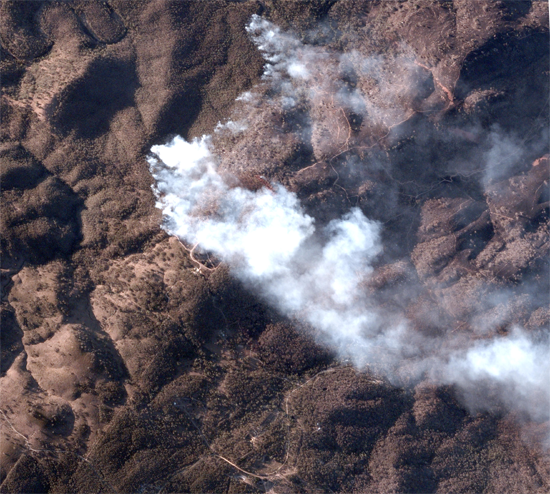

Bushfire in New South Wales, 8th March 2023. Captured by BlackSky.
Develop Sustainable Solutions
Data captured from satellites is useful in developing and implementing more sustainable solutions to existing industries. Data such as SAR and space-based LiDAR are applicable to creating sustainable agriculture plans by providing detailed and accurate terrain maps to optimise resources. Maintaining an understanding of field drainage and erosion patterns can help inspire better watering and fertiliser applications. With the increased value of carbon farming and carbon credits, satellite imagery data can provide a tool for existing carbon farms to be easily monitored and measured to ensure compliance and accuracy in carbon credit integrity. As mentioned above, urban heat islands are an increasing concern. Using satellite imagery can help to plan infrastructure and construction improvements to reduce urban heating, as well as enable continuous monitoring of the areas to evaluate the effectiveness of changes. Multisite monitoring employs timely, and regular satellite imagery to provide insight over multiple AOIs, in this case, high risk areas within urban heat islands. Consistently monitoring multiple AOIs allows climate professionals to track changes over long periods of time, empowering decision makers to make informed responses.

Areas of interest along Florida’s west coast during 2021 algal blooms. Captured by Landsat 8- OLI.
Arlula For Climate
Satellite imagery offers a unique perspective to gain insights and solve problems in land cover changes, human environmental impacts, and future climate-related events. Arlula’s platform has curated a global network of satellite imagery data providers in combination with a consolidated data management platform, giving users the power to derive actionable insights at scale with greater efficiency. Arlula can help power critical climate decisions from the field to the government desk.
Want to keep up-to-date?
Follow us on social media or sign up to our newsletter to keep up to date with new product releases and case studies.




